fpm(FastCGI Process Manager)を入れる前に、mysqlのメモリ設定を変更する。
vi /etc/mysql/my.cnf #query_cache_limit = 1M query_cache_limit = 12M #query_cache_size = 12M query_cache_size = 64M
service mysql restart
これ設定すると、エラーになるんだよな。書くファイルが間違ってるのかも。
apache apcに続いて、fpmをインストールする
a2enmod expires
service apache2 restart
vi /etc/apache2/apache2.conf 最終行に追加 # gzip setting AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE text/html text/plain text/css AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE text/javascript application/x-javascript application/javascript BrowserMatch ^Mozilla/4 gzip-only-text/html BrowserMatch ^Mozilla/4.0[678] no-gzip BrowserMatch \bMSIE !no-gzip !gzip-only-text/html # expire setting ExpiresActive On ExpiresDefault "access plus 1 year"
service apache2 restart
sudo apt-get install php7.0-fpm php7.0-mbstring sudo vi +760 /etc/php/7.0/fpm/php.ini # 760行目の「;cgi.fix_pathinfo=1」をデフォルトから変更 cgi.fix_pathinfo=0 sudo /etc/init.d/php7.0-fpm restart
mbstringも有効に
a2enmod proxy_fcgi setenvif a2enconf php7.0-fpm
/etc/php/7.0/fpm/pool.d/www.conf に記述があるか確認。無ければ追記する。 listen = /run/php/php7.0-fpm.sock
最後に、delfault-ssl.conf の VirtualHost内に追記する。
<FilesMatch "\.php$"> #SetHandler "proxy:fcgi://127.0.0.1:9000/" SetHandler "proxy:unix:/run/php/php7.0-fpm.sock|fcgi://localhost" </FilesMatch>
service apache2 restart
これで完了
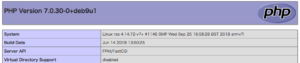
phpinfo()をみて、Server APIがFPM/FastCGI になっているのを確認
計測(https://tools.pingdom.com/)
| ras.viasv.com | www.club535.com | ||
| Server API | apache2.0Handler | FPM/FastCGI | CGI/FastCGI |
| Performance grade | C77 | C78 | C77 |
| Page size | 395.0KB | 395.5B | 613.7KB |
| Load time | 1.35s | 1.20s | 2.58s |
| Requests | 42 | 41 | 63 |